Toluene 99.9% – Industrial and Laboratory Grade Solvent
$29.99 – $290.00
Technical Specifications:
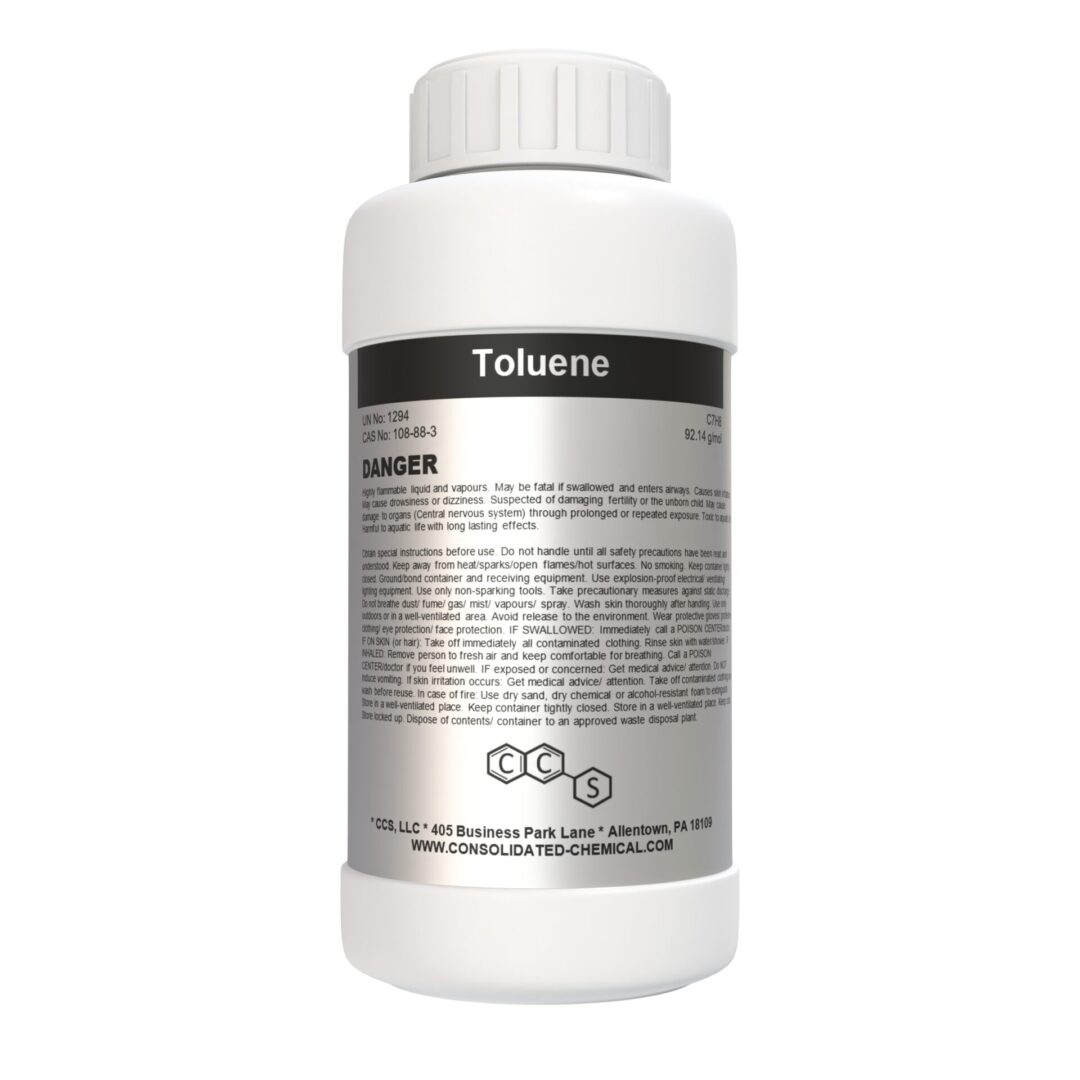
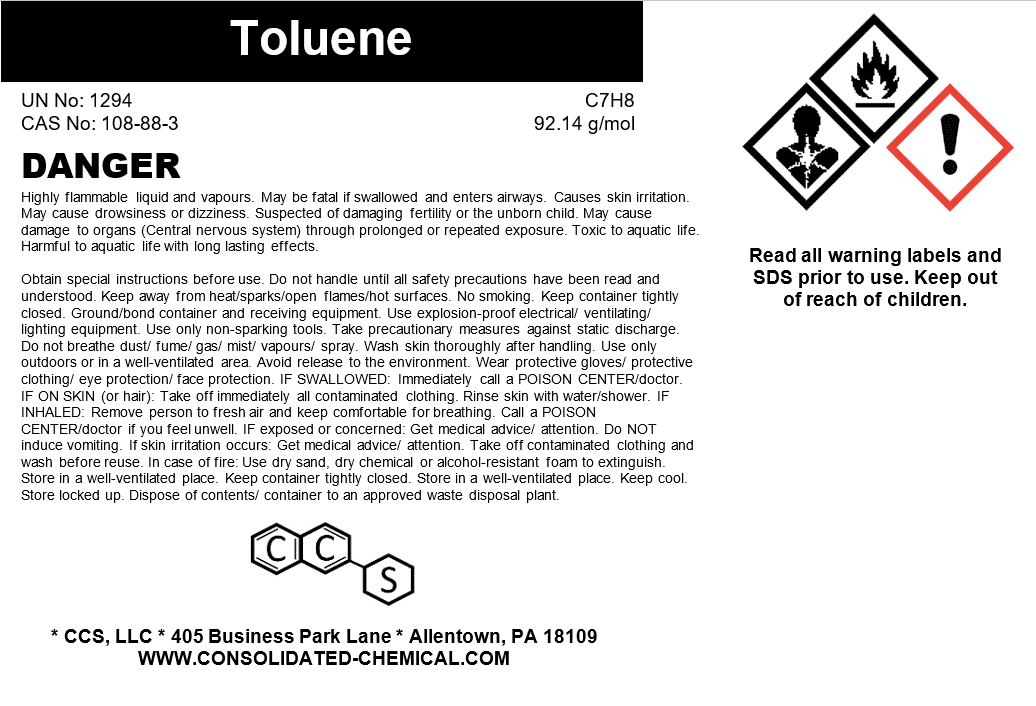
- Chemical Name: Toluene
- CAS Number: 108-88-3
- Molecular Formula: C₇H₈
- Molecular Weight: 92.14 g/mol
- Appearance: Clear, colorless liquid
- Odor: Sweet, aromatic odor
- Grade: Available in Industrial, Laboratory, and Reagent grades
- Boiling Point: 110.6°C (231.1°F)
- Melting Point: -95°C (-139°F)
- Density: 0.87 g/cm³ at 20°C
- Flash Point: 4°C (39°F) (closed cup)
- Refractive Index: 1.4969 at 20°C
- Vapor Pressure: 22 mmHg at 20°C
- Solubility: Insoluble in water; miscible with alcohol, ether, and most organic solvents
Chemical Properties:
- Aromatic Hydrocarbon: Belongs to the class of monoaromatic hydrocarbons, exhibiting excellent solvency for non-polar substances.
- Volatility: Moderate volatility, making it ideal for quick-drying applications in paints and coatings.
- Reactivity: Combustible; reacts with strong oxidizing agents and halogens.
Documents : Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
Description
Toluene is a high-purity, colorless, aromatic hydrocarbon solvent, widely used in various industrial applications due to its exceptional solvency properties. It is ideal for dissolving paints, coatings, adhesives, resins, and chemical reactants. With its distinctive sweet odor and versatility, toluene is a key component in chemical manufacturing and fuel industries.
Applications:
Solvent in Industrial Processes:
- Paints, Coatings, and Varnishes: Toluene is commonly used as a solvent in paints, varnishes, lacquers, and coatings due to its ability to dissolve many organic compounds, allowing for smooth application and fast drying.
- Adhesives: Toluene is a key solvent in adhesive formulations, especially in the manufacturing of rubber cements, contact adhesives, and model glues.
- Printing Inks: It serves as a solvent in printing inks for flexographic and gravure printing processes.
- Cleaning Agent: Toluene is used in industrial cleaning applications to remove oil, grease, and other residues from metal surfaces and machinery.
Chemical Intermediate:
- Benzene and Xylene Production: Toluene is used in the chemical industry to produce benzene and xylene through catalytic reforming and disproportionation processes.
- Toluene Diisocyanate (TDI): Toluene is used in the production of toluene diisocyanate, a key component in the manufacture of polyurethane foams used in furniture, mattresses, insulation, and automotive seating.
- Phenol and Benzoic Acid Production: It is also used as a precursor to synthesize other chemicals like phenol and benzoic acid.
Fuel Additive:
- Octane Booster in Gasoline: Used as a fuel additive to improve the octane rating of gasoline, helping to reduce engine knocking and improve performance. It is commonly added to high-performance fuels.
- Aviation Fuel: Toluene is sometimes added to aviation fuel to enhance performance in high-compression aircraft engines.
Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Active Ingredient Solvent: Toluene is used as a solvent in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds, particularly in the production of active ingredients, and as an extraction solvent in drug manufacturing processes.
Manufacture of Explosives:
- TNT (Trinitrotoluene): Toluene is used as a precursor in the production of trinitrotoluene (TNT), a well-known explosive material. This application is particularly important in military and mining industries.
Polymer and Plastic Production:
- Synthetic Rubber and Polymers: Toluene is involved in the production of synthetic rubber (like butadiene rubber) and plastics, particularly polystyrene. It acts as a solvent or as a starting material in the polymerization processes.
- Nylon and Polyurethane: Toluene is used in the production of caprolactam, a precursor to nylon, and as a feedstock for polyurethane production.
Laboratory Uses:
- Extraction Solvent: Toluene is often used in laboratories as a solvent for extractions and in analytical chemistry for separating and purifying organic compounds.
- Chromatography: It is used as a mobile phase or solvent in chromatography to help in the separation of chemical mixtures.
Electronics Industry:
- Cleaning Solvent: Toluene is used as a cleaning agent for circuit boards and electronic components due to its ability to dissolve residues, including fluxes used in soldering.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: It is employed in the manufacturing of semiconductors to clean and prepare surfaces for further processing.
Textile Industry:
- Fabric Coatings: Toluene is used in the formulation of coatings for textiles to make them water-resistant, durable, or glossy, especially in the production of synthetic fibers.
Leather Tanning and Processing:
- Leather Finishing: In the leather industry, toluene is used as a solvent in the finishing process to apply various coatings that give leather its smooth and polished appearance.
Paint Thinner:
- Diluent for Paints and Coatings: Frequently used as a paint thinner to adjust the viscosity of paints and coatings for better application and finish. It helps the paint flow smoothly and evaporates quickly after application.
Cosmetics and Personal Care:
- Nail Polish: Toluene is found in some nail polish formulations as a solvent to improve the smoothness and adhesion of the polish to nails. However, due to health concerns, its use in cosmetics has been regulated or replaced in many formulations.
Dye and Ink Production:
- Dissolving Pigments: Used to dissolve pigments and dyes, especially in the production of inks and dyes for the textile and printing industries.
Agriculture:
- Pesticide Formulation: Sometimes Used as a solvent in the formulation of agricultural chemicals, including herbicides and pesticides.
Aerospace Industry:
- Rocket Propellants: Toluene is used in the production of certain types of rocket propellants and fuel mixtures, particularly for high-performance aerospace applications.
Storage and Handling:
- Storage Conditions:
- Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area away from heat, open flames, and oxidizing agents.
- Use containers resistant to aromatic hydrocarbons, such as steel or HDPE.
- Shelf Life:
- Approximately 1-2 years when stored properly.
Additional information
| Size | 500mL (16 Fl Oz), 1000mL (32 Fl Oz), 1 Gallon (128 Fl Oz), 5 Gallon (640 Fl Oz) |
|---|
Related products
-

Methyl Alcohol (Methanol) – Premium Quality Multi-Purpose Solvent
$12.99 – $70.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Hexylene Glycol
$34.00 – $285.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Eucalyptol FCC High Purity Aroma Compound
$9.99 – $149.99 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Methyl Salicylate (Oil of Wintergreen) High Purity
$12.00 – $265.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page