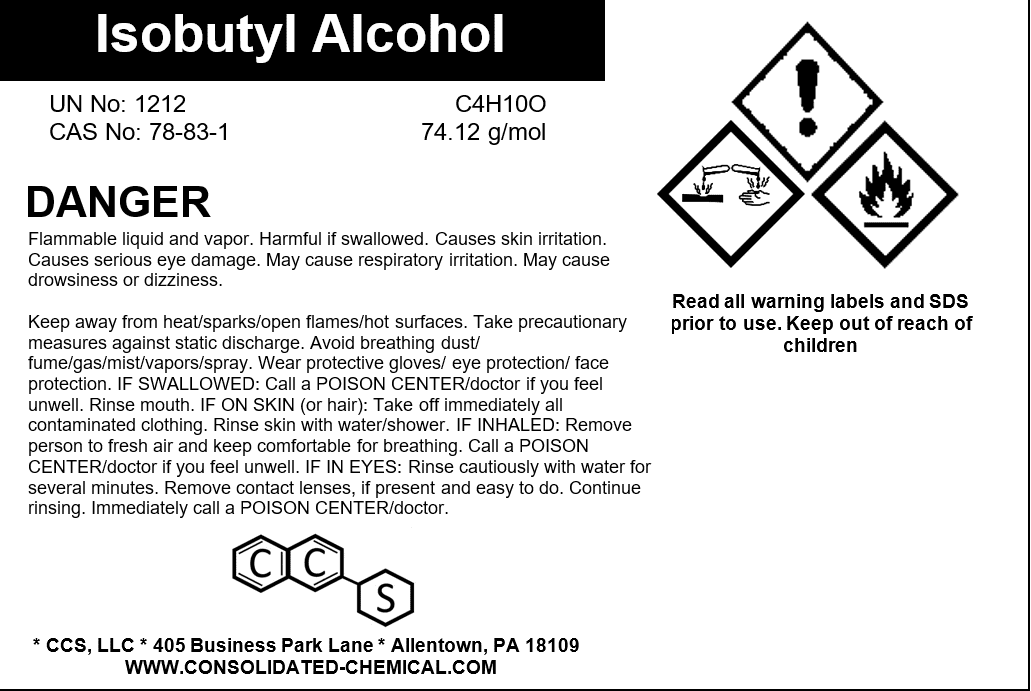
Description
Isobutyl Alcohol (2-Methyl-1-Propanol) is a high-purity solvent widely used in industrial, laboratory, and commercial applications. With its excellent solvency and versatility, it serves as a critical ingredient in coatings, cleaning formulations, adhesives, and chemical processes. Its moderate evaporation rate makes it suitable for various applications requiring precise drying properties.
Applications of Isobutyl Alcohol
Coatings and Paints
- Solvent:
- Improves flow, leveling, and drying in paints, varnishes, lacquers, and industrial coatings.
- Binder Component:
- Acts as a co-solvent to enhance the performance of resins and polymers.
Adhesives and Sealants
- Solvent:
- Enhances adhesion, stability, and application properties in adhesives and sealants.
Printing Inks
- Ink Formulation:
- Provides optimal viscosity and drying performance in printing inks for various surfaces.
Chemical Synthesis
- Intermediate:
- Used as a building block in the production of esters, pharmaceuticals, and other specialty chemicals.
- Reactant:
- Participates in esterification and other organic synthesis processes.
Industrial Cleaning
- Degreaser:
- Effective in cleaning machinery, tools, and equipment by dissolving oils and grease.
- Cleaning Agent:
- Used in formulations for household and industrial cleaning solutions.
Personal Care and Cosmetics
- Ingredient:
- Found in perfumes, hair sprays, and other personal care products for its solvency and quick-drying properties.
- Humectant:
- Retains moisture in cosmetic formulations, enhancing texture and stability.
Laboratory Use
- Solvent for Research:
- Used in sample preparation, chromatography, and other analytical techniques.
Pharmaceuticals
- Carrier Solvent:
- Facilitates the formulation and delivery of active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Agriculture
- Pesticide Formulations:
- Used as a solvent or carrier in certain agricultural chemicals.
Energy Sector
- Additive:
- Used in fuel and biofuel research and formulations.
Storage Instructions
- Temperature Control:
- Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area at temperatures below 25°C (77°F) to prevent evaporation and degradation.
- Avoid Ignition Sources:
- Keep away from open flames, sparks, and hot surfaces, as the product is flammable.
- Sealed Containers:
- Ensure containers are tightly closed to prevent vapor loss and contamination.
- Incompatibilities:
- Store away from strong oxidizing agents, acids, and reactive chemicals.
Handling Instructions
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Wear chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and a lab coat to prevent skin and eye contact.
- Use a respirator if handling in poorly ventilated areas.
- Ventilation:
- Handle in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to minimize vapor exposure.
- Safe Transfer:
- Use proper tools and containers for transfer to prevent spills and vapor release. Ground containers to avoid static discharge.
- Spill Management:
- For small spills: Absorb with inert materials such as sand or spill pads. Dispose of in accordance with local regulations.
- For large spills: Contain and collect for proper disposal. Avoid releasing into drains or waterways.
- Hygiene Practices:
- Wash hands thoroughly after handling. Avoid eating, drinking, or smoking in the handling area.
Precautions During Use
- Avoid inhalation of vapors or direct contact with skin and eyes.
- Use non-sparking tools and explosion-proof equipment in areas where vapors may accumulate.
Fire and Explosion Precautions
- Flammability: Flammable liquid and vapor. Keep away from ignition sources.
- Extinguishing Media: Use foam, CO₂, dry chemical, or water fog to extinguish fires.
- Firefighting: Wear self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) and full protective gear.
Disposal
Dispose of unused product, contaminated materials, and packaging in compliance with local, state, and federal regulations. Avoid releasing into drains, soil, or waterways.