Acetic Acid Glacial – High-Purity Acetic Acid
$14.99 – $69.99
General Information
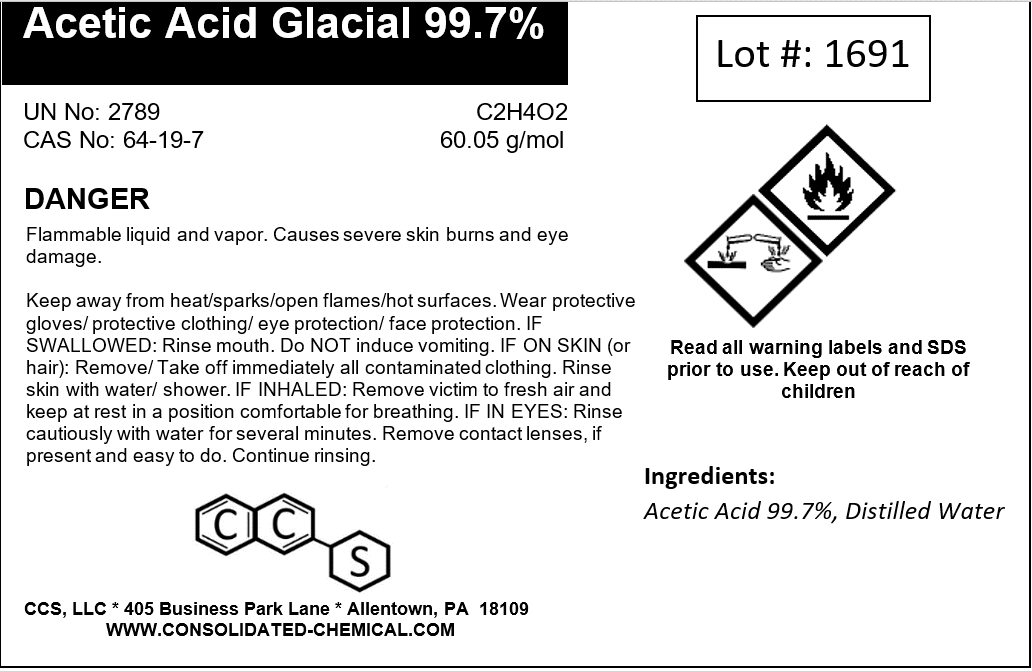
- Chemical Name: Acetic Acid Glacial
- Synonyms: Ethanoic Acid, Methanecarboxylic Acid
- Molecular Formula: CH₃COOH
- CAS Number: 64-19-7
- EC Number: 200-580-7
- Appearance: Clear, colorless liquid
- Odor: Strong vinegar-like odor
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Molecular Weight: 60.05 g/mol
- Purity: ≥99.5% (Glacial Grade)
- Density: 1.049 g/cm³ at 25°C
- Boiling Point: 118°C (244°F)
- Melting Point (Freezing Point): 16.6°C (62°F)
- Flash Point: 40°C (104°F) (closed cup)
- pH: ~2.4 (for 1% aqueous solution)
- Solubility:
- Fully miscible with water, alcohols, ethers, and many organic solvents.
Description
Acetic Acid Glacial is a highly concentrated form of acetic acid (99%+ purity) with a wide range of applications in laboratories, industrial processes, and manufacturing. Known for its exceptional quality and versatility, it is used in chemical synthesis, food processing (in regulated grades), cleaning, and as a pH regulator. This high-performance product meets stringent standards to ensure reliable and consistent results in all applications.
Applications of Acetic Acid Glacial
Chemical Synthesis
- Industrial Reagent:
- Used to manufacture acetate esters, acetic anhydride, and other organic compounds.
- Solvent:
- Effective in dissolving organic and inorganic compounds for various chemical reactions.
- Catalyst:
- Acts as a catalyst in esterification and polymerization processes.
Food and Beverage Industry (Regulated Grades)
- Food Additive (E260):
- Used as a preservative and acidity regulator in sauces, dressings, and pickling solutions.
- Flavoring Agent:
- Provides a sour taste in food products like vinegar-based condiments.
Laboratory Applications
- pH Control:
- Regulates pH in biochemical and analytical procedures.
- Chromatography:
- Commonly used as a solvent or buffer in liquid chromatography.
- Chemical Research:
- Essential for studying reaction mechanisms and developing new compounds.
Textile Industry
- Dyeing and Finishing:
- Used as a mordant to fix dyes onto fabrics and maintain color vibrancy.
- Fabric Processing:
- Improves the pH balance in textile treatments.
Industrial Uses
- Plastic Manufacturing:
- Integral in producing polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and cellulose acetate.
- Paints and Coatings:
- Acts as a solvent in paint, varnishes, and adhesives production.
Cleaning and Disinfection
- Industrial Cleaner:
- Used in descaling and cleaning machinery, pipes, and heat exchangers.
- Household Use:
- Effective for removing mineral deposits, rust stains, and grease.
Agriculture
- Pesticide Formulation:
- Used in weed control products as an effective herbicide in high concentrations.
- Soil Amendment:
- Helps regulate soil pH in agricultural settings.
Pharmaceuticals
- Drug Manufacturing:
- Intermediate in producing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
- Antimicrobial Agent:
- Utilized in medical settings for cleaning and sterilization.
Energy and Environmental Applications
- Battery Electrolytes:
- Used in certain rechargeable battery systems.
- Water Treatment:
- Plays a role in controlling pH in water treatment plants.
Education and Demonstrations
- Teaching Reagent:
- Used in schools and universities to demonstrate chemical reactions and properties.
Storage Guidelines
- Storage Conditions:
- Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from heat sources, open flames, and direct sunlight.
- Maintain storage temperature between 15°C and 25°C (59°F and 77°F).
- Keep the container tightly closed to prevent moisture absorption and contamination.
- Container Recommendations:
- Use containers made of glass, stainless steel, or high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
- Avoid using metal containers, as acetic acid is corrosive to certain metals.
- Incompatibilities:
- Keep away from strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, and reactive metals like aluminum and zinc.
Handling Guidelines
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Gloves: Use chemical-resistant gloves (nitrile, neoprene, or rubber).
- Eye Protection: Wear safety goggles or a face shield to prevent eye contact.
- Clothing: Use a lab coat or acid-resistant apron to protect skin.
- Workplace Safety:
- Handle in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to avoid inhalation of vapors.
- Avoid splashing and creating aerosols during handling.
- Precautionary Measures:
- Do not eat, drink, or smoke while handling acetic acid.
- Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
- Keep away from incompatible substances to prevent hazardous reactions.
Spill and Disposal Guidelines
- Spill Cleanup:
- For small spills:
- Neutralize with a weak base such as sodium bicarbonate or lime.
- Absorb with inert material like sand or vermiculite.
- For large spills:
- Evacuate the area and ventilate. Contain the spill and contact a chemical spill response team.
- For small spills:
- Disposal:
- Dispose of waste and contaminated materials in accordance with local, state, and federal regulations.
- Do not pour into drains or waterways.
Additional information
| Size | 100mL (3.3 Fl Oz), 250mL (8 Fl Oz), 500mL (16 Fl Oz), 1000mL (32 Fl Oz), 1 Gallon (128 Fl Oz) |
|---|
Related products
-

Triethyl Citrate HP Aroma/Flavor/Fragrance Compound
$12.00 – $150.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Ammonium Hydroxide 29% – Premium Aqueous Solution
$14.99 – $29.99 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Sodium Hydroxide Beads – Premium Quality Lye 1kg (2.2lb)
$22.00 Add to cart -

Beta-Pinene (Natural) – High-Purity Aroma Compound
$11.00 – $42.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page