Calcium Carbide Lumps 50g
$12.00
Chemical Information
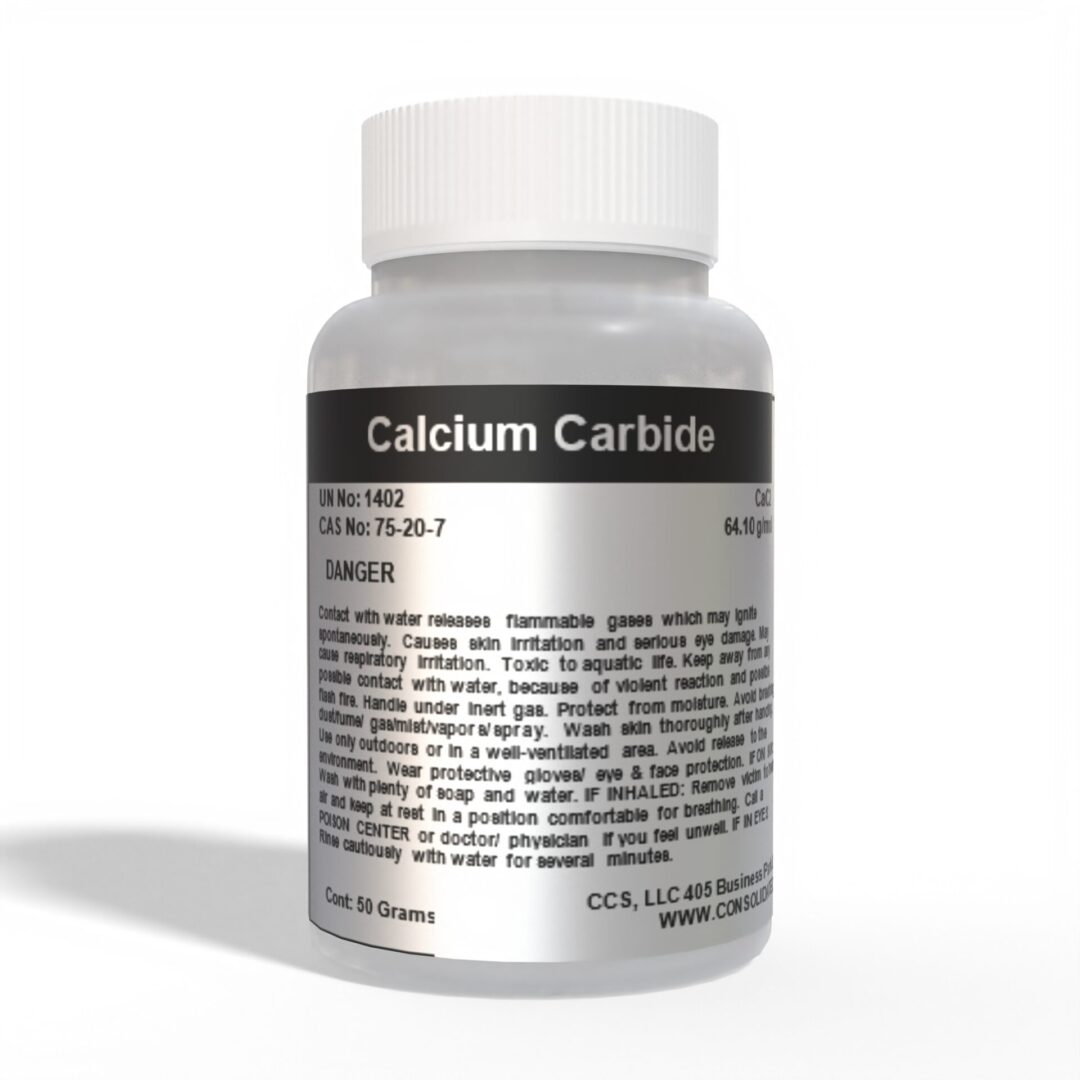
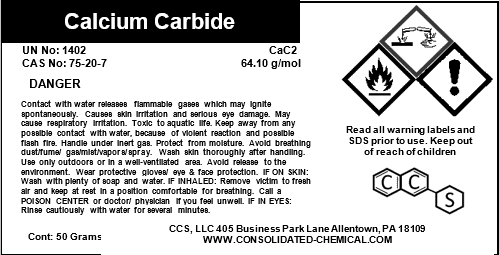
- Chemical Name: Calcium Carbide
- CAS Number: 75-20-7
- Molecular Formula: CaC₂
- Molecular Weight: 64.10 g/mol
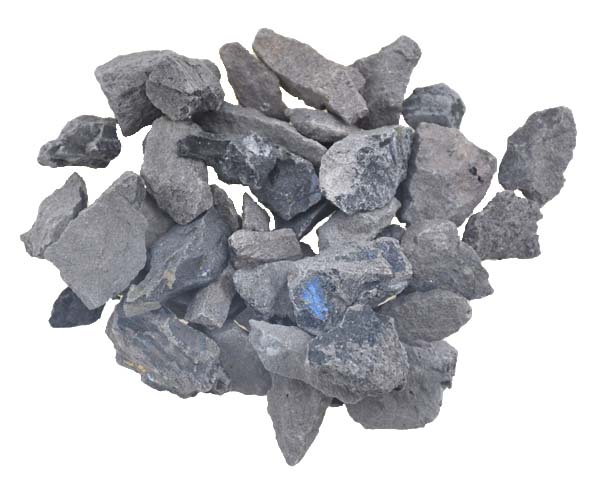
- Appearance: Grey to black solid lumps or powder
- Odor: Strong, garlic-like odor due to trace phosphine impurities
- Purity: 80-98% (Varies by grade)
Physical & Chemical Properties
- Density: 2.22 g/cm³
- Melting Point: 2,160°C (3,920°F)
- Boiling Point: Decomposes before boiling
- Solubility: Reacts violently with water to produce acetylene gas
- Reactivity: Strong reducing agent, highly reactive with moisture
- Gas Yield: 280-300 L/kg of acetylene gas
Mechanical & Stability Properties
- Thermal Stability: Stable under dry conditions
- Oxidation Resistance: Decomposes in humid environments
- Volatility: Non-volatile in solid state, highly reactive with water
- Compatibility: Reacts with acids, oxidizers, and water-containing materials
Description
Calcium Carbide is a gray or black solid substance that is commonly used in a variety of industrial applications. Upon contact with water, it reacts vigorously to produce acetylene gas (C₂H₂) and calcium hydroxide, making it an essential compound in welding, metal cutting, and various chemical processes. Calcium Carbide is also known for its role in producing acetylene gas for lighting and as a precursor in the production of chemicals and plastics.
Applications of Calcium Carbide:
1. Acetylene Gas Production
- Welding & Cutting: Used in oxy-acetylene torches for metal cutting and welding.
- Acetylene Generators: Produces high-purity acetylene gas for various industrial uses.
- Flame Hardening & Metal Processing: Used in industrial heating applications.
2. Metallurgical & Industrial Uses
- Steelmaking & Iron Production: Used as a reducing agent in steel manufacturing.
- Desulfurizing Agent: Removes impurities from molten iron and steel.
- Foundry & Metal Casting: Enhances carbon content in metal alloys.
3. Agriculture & Soil Treatment
- Fertilizer Production: Precursor for calcium cyanamide, used in soil conditioning.
- Weed & Pest Control: Applied in biopesticide formulations.
- Fruit Ripening Agent: Used in controlled-release applications for fruit maturation.
4. Chemical Synthesis & Industrial Processing
- Carbide Lamps: Generates acetylene gas for mining and underground lighting.
- Calcium Hydroxide Production: Forms slaked lime (Ca(OH)₂) for construction and chemical applications.
- Synthetic Rubber & Polymer Production: Acts as a key intermediate in specialty plastics manufacturing.
- Nanotechnology & Advanced Materials: Used in carbon nanostructure synthesis.
 Storage Guidelines:
Storage Guidelines:
- Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from moisture and water sources.
- Keep the container tightly sealed to prevent exposure to air and humidity, which can cause dangerous reactions.
- Store in non-reactive, airtight containers made of metal or high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
- Do not store near water, acids, oxidizing agents, or flammable materials.
- Recommended storage temperature: Between 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F).
- Store in a designated hazardous materials area, compliant with local regulations for flammable and reactive chemicals.
 Handling Precautions:
Handling Precautions:
- Avoid contact with water, as Calcium Carbide reacts with water to produce flammable acetylene gas.
- Handle with protective gloves, safety goggles, and chemical-resistant clothing to avoid skin and eye contact.
- Ensure the work area is well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of acetylene gas.
- Do not smoke or use open flames near Calcium Carbide, as acetylene gas is highly flammable.
- Use non-sparking tools to handle Calcium Carbide to reduce the risk of ignition.
- Avoid inhaling dust or fumes generated during handling.
 Avoid:
Avoid:
- Avoid moisture or water contact, including high humidity, to prevent gas production.
- Do not store near acids, oxidizers, or flammable substances.
- Avoid open flames, sparks, and static electricity in areas where Calcium Carbide is handled or stored.
- Do not store near food or drink.
 Container Management:
Container Management:
- Store in airtight, moisture-proof containers.
- Ensure containers are clearly labeled with hazard warnings, product name, and batch number.
- Regularly inspect containers for any signs of damage, corrosion, or leaks.
- Keep off the ground and store in dry, elevated areas to avoid accidental contact with water.
 Disposal Guidelines:
Disposal Guidelines:
Dispose in accordance with local, regional, and national regulations for hazardous chemical waste.
- Do not pour Calcium Carbide into drains or water sources.
- Use a certified hazardous waste disposal contractor for proper disposal.
Related products
-

Ammonium Hydroxide 29% – Premium Aqueous Solution
$14.99 – $29.99 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

1-Octanol (Alcohol C-8) Premium Aroma Fragrance Compound
$12.00 – $95.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Geraniol | High-Purity Fragrance/Aroma Compound
$9.99 – $800.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Cinnamic Acid – High Purity | Premium Quality
$14.99 – $48.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
SKU: 3675
Categories: Herbicide, Industrial Chemical, Pesticide
Tags: Acetylene Gas Production, Buy Calcium Carbide Online, calcium carbide, Calcium Carbide 50-80mm Lumps, calcium carbide acetylene generator, calcium carbide acetylene production, calcium carbide acetylene purity, calcium carbide advanced materials, calcium carbide Alibaba, calcium carbide alternative applications, calcium carbide Amazon, calcium carbide analytical reagent, calcium carbide as a desulfurizing agent, calcium carbide B2B marketplace, calcium carbide boiling point, Calcium Carbide Bulk, calcium carbide bulk storage, calcium carbide CAS 75-20-7, calcium carbide catalyst, calcium carbide chemical, Calcium Carbide Chemical Compound, calcium carbide chemical processing, calcium carbide chemical safety, calcium carbide chemical stability, calcium carbide competitive pricing, calcium carbide controlled handling, calcium carbide decomposition, calcium carbide decomposition products, calcium carbide demand, calcium carbide density, calcium carbide distributor, calcium carbide e-commerce, calcium carbide eBay, calcium carbide emergency response, calcium carbide emerging applications, calcium carbide energy applications, calcium carbide environmental impact, calcium carbide explosion risk, calcium carbide extended shelf life, calcium carbide extended stability, calcium carbide flammability, Calcium Carbide for Acetylene Gas, calcium carbide for acetylene gas welding, Calcium Carbide for Acetylene Lamps, Calcium Carbide for Acetylene Production, Calcium Carbide for Blacksmithing, Calcium Carbide for Chemical Synthesis, Calcium Carbide for Cutting Torches, Calcium Carbide for DIY Projects, Calcium Carbide for Emergency Lighting, Calcium Carbide for Explosive Testing, Calcium Carbide for Fishing, Calcium Carbide for Flame Cutting, Calcium Carbide for Fruit Ripening, Calcium Carbide for Fruit Ripening Process, calcium carbide for hydrogen generation, calcium carbide for industrial chemistry, Calcium Carbide for Industrial Use, Calcium Carbide for Labs, calcium carbide for material science, calcium carbide for metal cutting, Calcium Carbide for Metal Industry, Calcium Carbide for Mining, calcium carbide for oxy-acetylene welding, calcium carbide for removing impurities, Calcium Carbide for Steelmaking, calcium carbide for synthetic fibers, calcium carbide for synthetic rubber, calcium carbide for thermal insulation, Calcium Carbide for Torch Lighting, calcium carbide for underwater cutting, Calcium Carbide for Vintage Lanterns, Calcium Carbide for Water Reactivity, Calcium Carbide for Welding, Calcium Carbide for Welding Applications, calcium carbide formula, Calcium Carbide Gas Generator, calcium carbide gas production, calcium carbide GHS classification, calcium carbide global market, calcium carbide granules, calcium carbide grey solid, calcium carbide handling, Calcium Carbide Hazardous Material, Calcium Carbide High Purity, calcium carbide high-performance compound, calcium carbide high-temperature stability, calcium carbide hydrolysis, calcium carbide import export, calcium carbide in agriculture, calcium carbide in alternative fuels, calcium carbide in battery applications, calcium carbide in calcium cyanamide production, calcium carbide in calcium graphite production, calcium carbide in calcium hydroxide production, calcium carbide in carbide alloys, calcium carbide in carbide ceramics, calcium carbide in carbide lamps, calcium carbide in carbide lime, calcium carbide in carbon materials, calcium carbide in chemical industry, calcium carbide in chemical synthesis, calcium carbide in fertilizer manufacturing, calcium carbide in fuel additives, calcium carbide in industrial lighting, calcium carbide in iron production, calcium carbide in laboratory applications, calcium carbide in metallurgy, calcium carbide in nanotechnology, calcium carbide in organic compounds, calcium carbide in organic synthesis, calcium carbide in pharmaceuticals, calcium carbide in refractory applications, calcium carbide in soil conditioning, calcium carbide in steelmaking, calcium carbide in water reaction, calcium carbide in water treatment, calcium carbide in welding, calcium carbide industrial applications, calcium carbide industrial standards, calcium carbide industrial supply, calcium carbide industrial-grade, calcium carbide industry trends, calcium carbide innovation, calcium carbide innovations, calcium carbide IUPAC name, calcium carbide lab reagent, calcium carbide lump, Calcium Carbide Lumps, calcium carbide manufacturer, calcium carbide market growth, calcium carbide melting point, calcium carbide mining lamps, calcium carbide molecular weight, calcium carbide MSDS, calcium carbide odor, calcium carbide oxidation resistance, Calcium Carbide Powder, calcium carbide precautions, calcium carbide price, calcium carbide procurement, calcium carbide REACH compliance, calcium carbide reactivity, calcium carbide reducing agent, calcium carbide regulatory compliance, calcium carbide research, calcium carbide safe usage, Calcium Carbide Safety, calcium carbide safety data, calcium carbide safety precautions, calcium carbide SDS, calcium carbide solubility, calcium carbide sourcing, Calcium Carbide Stones, calcium carbide storage, Calcium Carbide Supplier, calcium carbide synonyms, calcium carbide toxic effects, calcium carbide trade, calcium carbide transportation, calcium carbide usage guidelines, Calcium Carbide Uses, calcium carbide Walmart, calcium carbide white solid, calcium carbide wholesale, calcium carbide worldwide shipping, fertilizer, Industrial Grade Calcium Carbide, lamps, pineapple, steelmaking