Copper (II) Chloride Dihydrate
$24.99 – $38.00
General Information
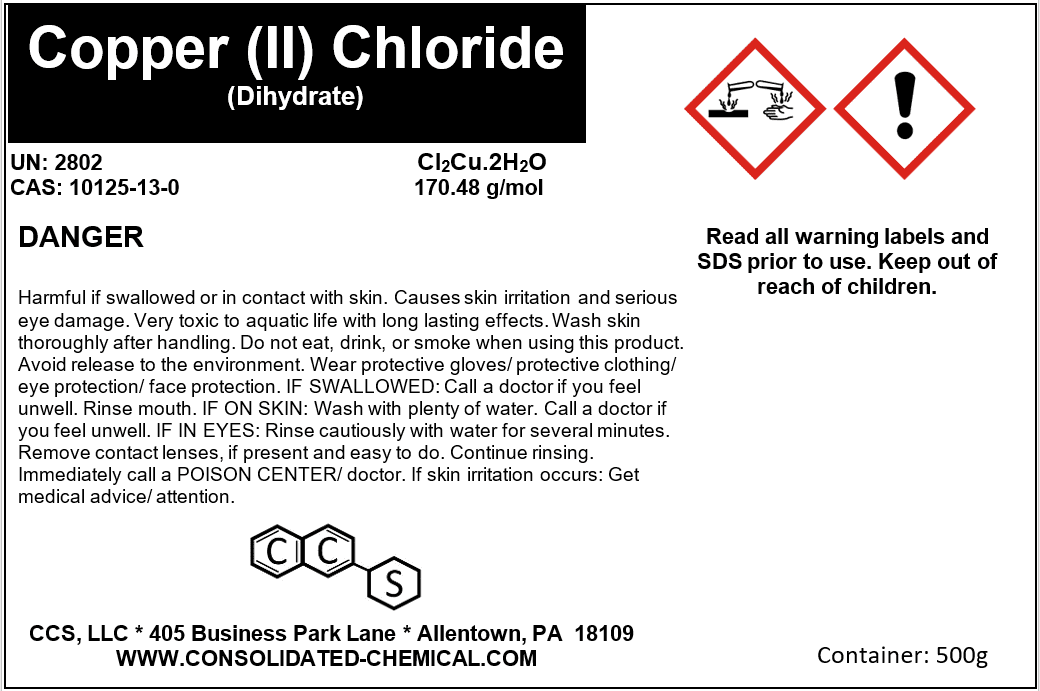
- Chemical Name: Copper (II) Chloride Dihydrate
- Synonyms: Cupric Chloride Dihydrate
- Molecular Formula: CuCl₂·2H₂O
- CAS Number: 10125-13-0
- EC Number: 231-210-2
- Appearance: Blue-green crystalline powder
- Odor: Odorless
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Molecular Weight: 170.48 g/mol
- Boiling Point: Decomposes before boiling
- Melting Point: ~100°C (loss of water of crystallization)
- Density: 2.54 g/cm³ at 25°C
- Solubility:
- Water: Highly soluble (~76 g/100 mL at 25°C)
- Soluble in ethanol, acetone, and other polar solvents.
- pH (1% Aqueous Solution): ~3–4 (acidic solution)
Purity and Grade
- Purity: ≥98%
- Grade: Laboratory grade, industrial grade
Description
Copper (II) Chloride Dihydrate is a high-purity inorganic compound widely used in laboratories, research, and industrial applications. Known for its versatility, it serves as a reagent, catalyst, and intermediate in chemical processes. With excellent solubility and consistent performance, this compound is a reliable choice for professionals across various industries.
Applications of Copper (II) Chloride Dihydrate
Laboratory and Research
- Reagent in Chemical Synthesis:
- Commonly used in reactions involving oxidation and chlorination.
- Analytical Chemistry:
- Utilized for qualitative and quantitative analysis of copper ions and other compounds.
Catalysis
- Catalyst in Organic Reactions:
- Used in the synthesis of organochlorides and other complex organic compounds.
- Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Catalysis:
- Plays a role in oxidation and coupling reactions.
Electronics Industry
- Etching Agent:
- Used in printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing for etching copper layers.
- Conductive Materials:
- Involved in producing copper-based conductive inks and coatings.
Industrial Applications
- Pigment and Dye Production:
- Acts as an intermediate in manufacturing blue and green pigments.
- Chemical Manufacturing:
- A precursor for other copper-based chemicals.
Textile Industry
- Mordant for Dyeing:
- Enhances the bonding of dyes to fabrics, especially in natural and synthetic fibers.
Agriculture
- Micronutrient in Fertilizers:
- Provides essential copper for plant growth and metabolic processes.
- Fungicide Formulations:
- Used in agricultural sprays to control fungal diseases in crops.
Water Treatment
- Algaecide:
- Controls algae growth in water systems, including ponds and swimming pools.
Photochemistry
- Light Sensitivity Applications:
- Used in certain photochemical experiments and applications.
Education and Demonstration
- Demonstration of Chemical Properties:
- Ideal for teaching redox reactions, solubility, and coordination chemistry in academic settings.
Metal Surface Treatment
- Electroplating:
- Used in copper electroplating to enhance surface properties of metals.
Storage Guidelines
- Storage Conditions:
- Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area away from heat, direct sunlight, and sources of moisture.
- Maintain storage temperature between 15°C and 25°C (59°F and 77°F).
- Keep the container tightly sealed to prevent contamination and moisture absorption.
- Container Recommendations:
- Use containers made of non-reactive materials such as glass or polyethylene.
- Ensure containers are clearly labeled to avoid accidental misuse.
- Incompatibilities:
- Avoid contact with strong oxidizers, strong bases, and reactive metals.
- Protect from exposure to acids, as it may release toxic chlorine gas.
Handling Guidelines
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Gloves: Wear nitrile or neoprene gloves to prevent skin contact.
- Eye Protection: Use chemical splash goggles to protect eyes.
- Clothing: Wear a lab coat or protective apron to minimize skin exposure.
- Workplace Safety:
- Handle in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to minimize inhalation of dust or fumes.
- Avoid creating or inhaling dust.
- Precautionary Measures:
- Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
- Do not eat, drink, or smoke while handling the material.
- Prevent spillage to avoid contamination of surfaces or equipment.
Spill and Disposal Guidelines
- Spill Cleanup:
- Contain spills with an inert absorbent material such as sand or vermiculite.
- Scoop up the material and place it in a labeled container for disposal.
- Disposal:
- Dispose of in accordance with local, state, and federal regulations.
- Do not release into sewers, waterways, or the environment.
Additional information
| Size | 250 Grams, 500 Grams, 1000 Grams |
|---|
Related products
-

Butyl Alcohol (Butanol) – Premium Grade Solvent
$24.00 – $120.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Methyl Salicylate (Oil of Wintergreen)
$12.00 – $265.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Myrcene (100% Natural Extract) – Premium Aroma Compound
$17.00 – $380.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Copper Sulfate Pentahydrate | Food/Feed Grade
$19.99 – $49.99 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
SKU: N/A
Category: Uncategorized
Tags: Affordable Copper Chloride, Blue-Green Copper Chloride, Bulk Copper Chloride Supplier, Buy Copper Chloride Online, Copper (II) Chloride Dihydrate, Copper Chloride for Agriculture, Copper Chloride for Analytical Chemistry, Copper Chloride for Catalysis, Copper Chloride for Chemical Synthesis, Copper Chloride for Dyes, Copper Chloride for Educational Use, Copper Chloride for Electroplating, Copper Chloride for Fertilizers, Copper Chloride for Fungicides, Copper Chloride for Industrial Applications, Copper Chloride for Laboratories, Copper Chloride for Light Sensitivity, Copper Chloride for Metal Surface Treatment, Copper Chloride for Organic Reactions, Copper Chloride for PCB Etching, Copper Chloride for Pigments, Copper Chloride for Redox Reactions, Copper Chloride for Research, Copper Chloride for Textile Dyeing, Cupric Chloride Dihydrate, Eco-Friendly Copper Chloride Packaging, High-Purity Copper Chloride, Industrial-Grade Copper Chloride, Laboratory-Grade Copper Chloride, Long Shelf-Life Copper Chloride, Safe Handling Copper Chloride, Water-Soluble Copper Chloride