Oxalyl Chloride – High-Purity Reagent for Chemical Synthesis
$200.00
General Information
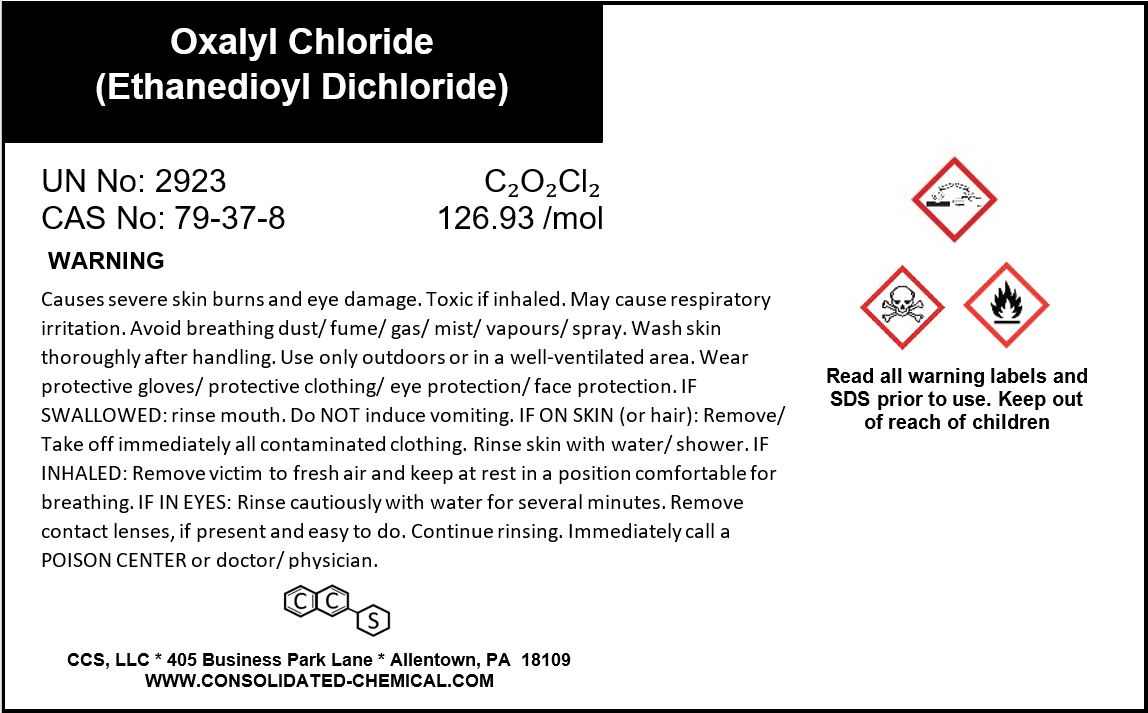
- Chemical Name: Oxalyl Chloride
- IUPAC Name: Ethanedioyl dichloride
- CAS Number: 79-37-8
- Molecular Formula: C₂O₂Cl₂
- Molecular Weight: 126.93 g/mol
- Synonyms: Carbonyl Chloride, Ethanedioic Acid Dichloride
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Appearance: Colorless to pale yellow liquid
- Odor: Pungent, acrid
- Density: ~1.48 g/cm³ at 20°C
- Boiling Point: 63–64°C
- Melting Point: -12°C
- Vapor Pressure: ~139 mmHg at 20°C
- Flash Point: Highly flammable
- Refractive Index: ~1.401 at 20°C
- Solubility:
- Reacts violently with water, producing hydrochloric acid and carbon dioxide
- Soluble in organic solvents like benzene and chloroform
Chemical Properties
- Reactivity:
- Reacts with water, alcohols, and amines, producing corresponding acid derivatives.
- Highly reactive and corrosive.
- Stability: Stable under inert, dry conditions; decomposes in the presence of moisture.
- Hazardous Byproducts: Hydrochloric acid and phosgene gas when decomposed.
Description
Oxalyl Chloride is a versatile, high-purity reagent commonly used in organic synthesis, particularly for converting carboxylic acids to acid chlorides and esters. With its reactive properties, it serves as a crucial component in the pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and specialty chemical industries.
Applications for Oxalyl Chloride:
- Organic Synthesis:
- Acid Chloride Preparation: Converts carboxylic acids to acid chlorides, which are precursors for esters, amides, and other derivatives.
- Esterification and Amidation Reactions: Facilitates the synthesis of esters and amides used in pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals.
- Vilsmeier-Haack Reaction: Key reagent for converting aromatic compounds into aldehydes.
- Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Used in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
- Essential for creating intermediates in drug production.
- Facilitates the development of specialty compounds for research and therapeutic use.
- Agrochemical Industry:
- Plays a role in the synthesis of pesticides, herbicides, and insecticides.
- Used to create key intermediates for crop protection chemicals.
- Polymer and Material Science:
- Employed in the modification of polymers and resins to enhance performance and durability.
- Useful in producing specialty coatings and adhesives.
- Specialty Chemicals:
- Utilized in the production of dyes, fragrances, and flavor compounds.
- Enables the creation of custom fine chemicals for niche applications.
- Textile Industry:
- Used to produce intermediates for fabric treatments and finishes.
- Research and Development:
- A critical reagent for laboratory-scale synthesis and exploratory research in organic chemistry.
- Used in academic and industrial research for developing new chemical methodologies.
- Industrial Applications:
- Employed in the production of advanced materials, including high-performance composites and coatings.
- Integral to manufacturing processes that require reactive intermediates.
Storage:
- Temperature: Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area. Ideal storage temperature is 2–8°C (35–46°F) to prevent decomposition.
- Containers:
- Use tightly sealed containers made of compatible materials such as glass or Teflon-lined containers.
- Avoid metal containers, as Oxalyl Chloride is corrosive to most metals.
- Location:
- Keep away from moisture, direct sunlight, and heat sources.
- Store separately from water, alcohols, amines, and other incompatible substances to prevent hazardous reactions.
- Labeling: Clearly label containers with hazard warnings and proper storage instructions.
Handling:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Eye Protection: Chemical splash goggles or a full-face shield.
- Skin Protection: Chemical-resistant gloves (e.g., nitrile or butyl rubber) and protective clothing.
- Respiratory Protection: Use a respirator approved for acid gases when working in areas with poor ventilation or potential vapor exposure.
- Ventilation: Always handle Oxalyl Chloride in a fume hood or a well-ventilated area to minimize exposure to vapors.
- Safe Practices:
- Avoid inhalation, ingestion, and contact with skin or eyes.
- Handle carefully to prevent spills or leaks, as Oxalyl Chloride reacts violently with water, releasing toxic gases (e.g., hydrogen chloride and carbon monoxide).
- Do not open containers in humid conditions to avoid moisture-induced reactions.
Spill and Leak Management:
- Small Spills:
- Absorb using an inert material such as dry sand or vermiculite.
- Neutralize residues with a suitable agent (e.g., soda ash or lime).
- Dispose of waste according to local regulations.
- Large Spills:
- Evacuate the area and restrict access.
- Ensure proper ventilation and wear full protective gear, including a respirator.
- Contain and neutralize the spill before cleanup.
Disposal:
Dispose of Oxalyl Chloride and its residues in compliance with local, state, and federal regulations. Ensure disposal by a licensed hazardous waste disposal service.
Additional information
| Size | 100mL (3.3 Fl Oz) |
|---|
Related products
-

N-Heptane – High Purity Bestine Thinner
$14.00 – $67.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Potassium Phosphate, Dibasic – Food Grade Additive
$14.99 – $27.99 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Methylene Blue Stain/Dye High Purity, Poly Bottle, 10g-50g
$12.50 – $34.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Methyl Alcohol (Methanol) – Premium Multi-Purpose Solvent
$12.99 – $70.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
SKU: N/A
Categories: Herbicide, Industrial Chemical, Pesticide, Research
Tags: buy oxalyl chloride, Fine Chemical Oxalyl Chloride, High-Purity Oxalyl Chloride, Industrial Grade Oxalyl Chloride, Moisture-Sensitive Oxalyl Chloride, Oxalyl Chloride, Oxalyl Chloride Acid Chloride Agent, Oxalyl Chloride Bulk Supplier, Oxalyl Chloride CAS 79-37-8, oxalyl chloride chemical, oxalyl chloride distributor, oxalyl chloride for acid chlorides, oxalyl chloride for adhesives, Oxalyl Chloride for Advanced Chemistry, oxalyl chloride for advanced composites, oxalyl chloride for advanced manufacturing, oxalyl chloride for advanced materials, oxalyl chloride for aerospace applications, oxalyl chloride for aerospace coatings, Oxalyl Chloride for Agrochemical Production, oxalyl chloride for agrochemical research, oxalyl chloride for agrochemicals, oxalyl chloride for AI-driven chemistry, Oxalyl Chloride for Amidation, oxalyl chloride for analytical research, oxalyl chloride for antimicrobial applications, oxalyl chloride for antimicrobial coatings, oxalyl chloride for antimicrobial textiles, oxalyl chloride for automotive coatings, oxalyl chloride for automotive industry, oxalyl chloride for battery materials, oxalyl chloride for bio-based chemicals, oxalyl chloride for biochemical synthesis, oxalyl chloride for biodegradable materials, oxalyl chloride for biodegradable products, oxalyl chloride for biofuel production, oxalyl chloride for biomedical research, oxalyl chloride for biopharmaceuticals, oxalyl chloride for biopolymers, oxalyl chloride for biosensors, oxalyl chloride for building materials, oxalyl chloride for carbonylation, oxalyl chloride for catalyst development, oxalyl chloride for catalyst production, oxalyl chloride for ceramic processing, oxalyl chloride for chemical engineering, oxalyl chloride for chemical formulations, oxalyl chloride for chemical intermediates, oxalyl chloride for chemical manufacturing, oxalyl chloride for chemical synthesis, Oxalyl Chloride for Coatings, oxalyl chloride for composite materials, oxalyl chloride for conductive materials, oxalyl chloride for construction chemicals, oxalyl chloride for controlled release formulations, oxalyl chloride for corrosion inhibitors, oxalyl chloride for cosmetic chemistry, oxalyl chloride for cosmetic formulations, oxalyl chloride for crop protection, Oxalyl Chloride for Custom Applications., oxalyl chloride for diagnostic reagents, oxalyl chloride for drilling fluids, oxalyl chloride for drug synthesis, Oxalyl Chloride for Dyes, oxalyl chloride for dyes and pigments, oxalyl chloride for eco-friendly formulations, oxalyl chloride for electric vehicle components, oxalyl chloride for electrochemistry, oxalyl chloride for electronic circuits, oxalyl chloride for electronic materials, oxalyl chloride for electroplating, oxalyl chloride for emerging technologies, oxalyl chloride for energy storage, oxalyl chloride for environmental science, oxalyl chloride for enzyme research, Oxalyl Chloride for Esterification, oxalyl chloride for fertilizer additives, oxalyl chloride for fine chemicals, oxalyl chloride for flame retardants, oxalyl chloride for fluorination reactions, oxalyl chloride for food additives, oxalyl chloride for food processing, oxalyl chloride for fragrance manufacturing, oxalyl chloride for fuel additives, oxalyl chloride for fuel cell technology, oxalyl chloride for green chemistry, oxalyl chloride for green solvents, oxalyl chloride for heat-resistant materials, oxalyl chloride for herbicide production, oxalyl chloride for high-performance adhesives, oxalyl chloride for high-performance materials, oxalyl chloride for high-performance surfactants, oxalyl chloride for high-temperature coatings, oxalyl chloride for histology, oxalyl chloride for hospital-grade disinfectants, oxalyl chloride for hydrogen production, oxalyl chloride for immunology research, oxalyl chloride for industrial applications, oxalyl chloride for industrial cleaning, oxalyl chloride for industrial coatings, oxalyl chloride for industrial filtration, oxalyl chloride for industrial lubricants, oxalyl chloride for industrial processes, oxalyl chloride for industrial R&D, oxalyl chloride for industrial solvents, oxalyl chloride for ink manufacturing, Oxalyl Chloride for Laboratory Research, oxalyl chloride for laboratory use, oxalyl chloride for lithium-ion batteries, oxalyl chloride for lubricants, Oxalyl Chloride for Material Science, oxalyl chloride for medical applications, oxalyl chloride for medical coatings, oxalyl chloride for medical devices, oxalyl chloride for medical imaging, oxalyl chloride for medical research, oxalyl chloride for metallurgy, oxalyl chloride for nanocoatings, oxalyl chloride for nanomaterials, oxalyl chloride for nanotechnology, oxalyl chloride for non-toxic coatings, oxalyl chloride for oilfield chemicals, oxalyl chloride for optical materials, oxalyl chloride for optics manufacturing, Oxalyl Chloride for Organic Synthesis, oxalyl chloride for peptide coupling, oxalyl chloride for peptide research, oxalyl chloride for peptide synthesis, oxalyl chloride for pesticide synthesis, oxalyl chloride for petrochemical refining, oxalyl chloride for pharmaceutical excipients, oxalyl chloride for pharmaceutical industry, oxalyl chloride for pharmaceutical intermediates, oxalyl chloride for pharmaceutical raw materials, Oxalyl Chloride for Pharmaceutical Synthesis, oxalyl chloride for pharmaceuticals, oxalyl chloride for photopolymerization, oxalyl chloride for pollution control, oxalyl chloride for polymer modification, oxalyl chloride for polymer production, oxalyl chloride for polymer science, Oxalyl Chloride for Polymer Synthesis, oxalyl chloride for protective coatings, oxalyl chloride for reagent synthesis, oxalyl chloride for recycling processes, oxalyl chloride for refinery applications, oxalyl chloride for renewable chemistry, oxalyl chloride for renewable energy, oxalyl chloride for resins, oxalyl chloride for robotic materials, oxalyl chloride for seed treatments, oxalyl chloride for semiconductor fabrication, oxalyl chloride for semiconductor processing, oxalyl chloride for smart materials, oxalyl chloride for smart polymers, oxalyl chloride for smart textiles, oxalyl chloride for sol-gel processing, oxalyl chloride for specialty adhesives, oxalyl chloride for specialty chemicals, oxalyl chloride for specialty resins, oxalyl chloride for structural adhesives, oxalyl chloride for surface coatings, oxalyl chloride for surface treatment, oxalyl chloride for sustainability applications, oxalyl chloride for sustainable coatings, oxalyl chloride for synthetic chemistry, oxalyl chloride for textile finishing, oxalyl chloride for textile industry, oxalyl chloride for tissue engineering, oxalyl chloride for UV-resistant coatings, oxalyl chloride for veterinary medicine, Oxalyl Chloride for Vilsmeier Reaction, oxalyl chloride for waste treatment, oxalyl chloride for water purification, oxalyl chloride for water treatment, oxalyl chloride high purity, oxalyl chloride industrial grade, Oxalyl Chloride Manufacturer, oxalyl chloride online supplier, Oxalyl Chloride Reagent, oxalyl chloride reagent grade, oxalyl chloride wholesale, Reactive Oxalyl Chloride, Specialty Oxalyl Chloride