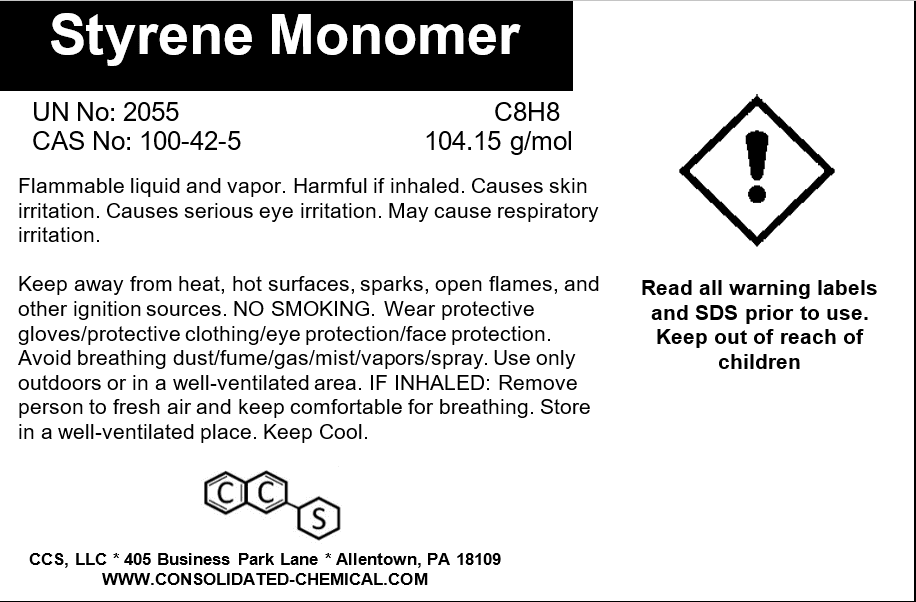
Styrene Monomer – High-Purity Industrial Grade
$13.00 – $23.00
General Information
- Chemical Name: Styrene Monomer
- Synonyms: Vinylbenzene, Ethenylbenzene, Phenylethene
- CAS Number: 100-42-5
- EC Number: 202-851-5
- Molecular Formula: C₈H₈
- Molecular Weight: 104.15 g/mol
- Grade: Industrial Grade
Physical Properties
- Appearance: Clear, colorless to pale yellow liquid
- Odor: Sweet, aromatic odor
- Purity: ≥ 99%
- Density: ~0.91 g/cm³ at 20°C
- Boiling Point: ~145°C
- Melting Point: -31°C
- Flash Point: 31°C (Closed Cup)
- Refractive Index: 1.546–1.548 at 20°C
- Vapor Pressure: 6.4 mmHg at 20°C
- Autoignition Temperature: ~490°C
- Solubility:
- Insoluble in water
- Soluble in alcohols, ethers, and most organic solvents
Chemical Properties
- Stability:
- Stable under recommended storage conditions.
- Prone to polymerization if exposed to heat, light, or air without stabilizers.
- Polymerization Inhibitor: Typically stabilized with 4-tert-Butylcatechol (TBC) to prevent premature polymerization.
Description
Our Styrene Monomer is a high-purity, industrial-grade organic compound widely used as a chemical feedstock in the production of polymers, resins, and elastomers. Its excellent reactivity and stability make it an essential raw material in various industrial processes, including the manufacturing of plastics, coatings, and synthetic rubbers.
Applications of Styrene Monomer – High-Purity Industrial Grade
Polymer and Plastic Manufacturing
- Polystyrene Production:
- A primary raw material for producing general-purpose polystyrene (GPPS) and high-impact polystyrene (HIPS) used in packaging, consumer goods, and electronics.
- ABS and SAN Plastics:
- Essential in the production of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) and Styrene Acrylonitrile (SAN) plastics for automotive parts, appliances, and toys.
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS):
- Used in foam products such as insulation materials, disposable food containers, and protective packaging.
Resin and Coatings Industry
- Unsaturated Polyester Resins:
- Serves as a reactive solvent in unsaturated polyester resins for composite materials, fiberglass products, and marine applications.
- Vinyl Ester Resins:
- A critical ingredient in resins for coatings, adhesives, and corrosion-resistant applications.
Rubber and Elastomer Production
- Synthetic Rubber:
- A key component in the production of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) used in tires, footwear, and conveyor belts.
- Thermoplastic Elastomers:
- Used in creating durable and flexible elastomeric materials.
Chemical Synthesis
- Chemical Intermediate:
- Used in the synthesis of various organic chemicals, including styrene derivatives for specialty applications.
Adhesives and Sealants
- Reactive Diluent:
- Acts as a solvent in the formulation of adhesives and sealants, ensuring easy application and enhanced performance.
Coatings and Paints
- Solvent in Industrial Coatings:
- Provides optimal flow and drying characteristics in paints and industrial coatings.
Construction Materials
- Insulation and Building Components:
- Used in the production of expanded and extruded polystyrene foams for energy-efficient insulation.
Electrical and Electronics
- Housing and Enclosures:
- Integral in manufacturing durable housings for electronic devices.
Storage Instructions
- Temperature Control:
- Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area at temperatures below 25°C (77°F) to minimize polymerization risk.
- Protect from Light:
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight and UV light, as these can trigger unwanted polymerization.
- Sealed Containers:
- Keep containers tightly closed when not in use to prevent vapor release and contamination.
- Inhibitor Use:
- Use 4-tert-Butylcatechol (TBC) or similar inhibitors in storage containers to prevent polymerization.
- Compatibility:
- Store away from oxidizing agents, strong acids, bases, and ignition sources.
- Fire Safety:
- Ensure storage areas are equipped with fire suppression systems. Avoid storing near flammable or combustible materials.
Handling Instructions
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Always wear chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and chemical-resistant clothing to avoid skin and eye contact.
- Use a respirator or work under a fume hood in areas with insufficient ventilation.
- Ventilation:
- Handle in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to minimize exposure to vapors.
- Avoid Ignition Sources:
- Do not smoke or use open flames near the product. Use non-sparking tools and explosion-proof equipment.
- Safe Transfer:
- Use grounded and bonded containers and transfer equipment to avoid static discharge during handling.
- Spill Management:
- Contain spills immediately using inert absorbent materials like sand or vermiculite. Dispose of waste in accordance with local regulations.
- Hygiene Practices:
- Wash hands thoroughly after handling. Avoid eating, drinking, or smoking in the handling area.
Disposal
Dispose of Styrene Monomer and any contaminated materials in accordance with local, state, and federal regulations. Avoid releasing the product into drains, waterways, or soil.
Additional information
| Size | 100mL (3.3 Fl Oz), 250mL (8 Fl Oz), 500mL (16 Fl Oz) |
|---|
Related products
-

Triethyl Citrate HP Aroma/Flavor/Fragrance Compound
$12.00 – $150.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Sodium Silicate 40% Solution
$16.00 – $59.99 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Ferric Chloride Solution Liquid Etchant
$14.00 – $200.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Eucalyptol – FCC High Purity Aroma Compound
$9.99 – $149.99 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page