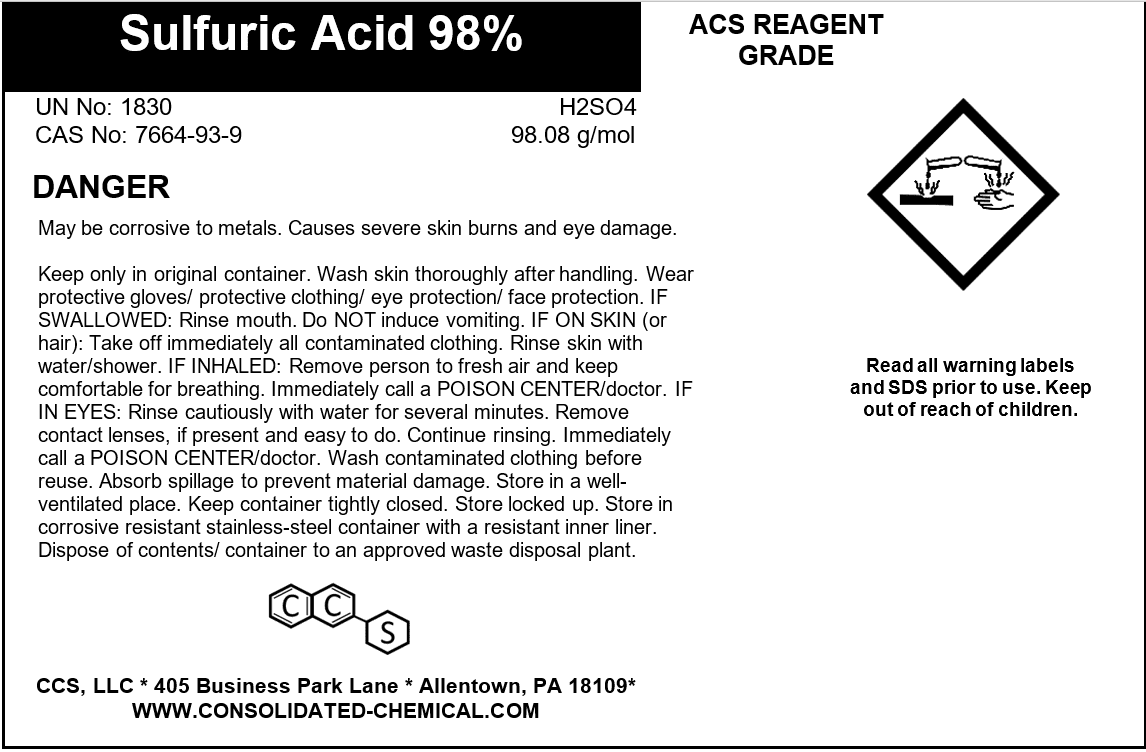
Sulfuric Acid 98% ACS Grade
$14.99 – $45.00
Chemical Information:
- Chemical Name: Sulfuric Acid
- Grade: ACS (American Chemical Society) Grade
- Formula: H₂SO₄
- CAS Number: 7664-93-9
- Concentration: 98% by weight
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Clear, colorless to slightly yellow liquid
- Density: ~1.84 g/cm³ at 20°C (68°F)
- Boiling Point: 290°C (554°F)
- Melting Point: ~10°C (50°F)
- Viscosity: ~26.7 cP at 20°C (68°F)
- Odor: Odorless, though it can emit slight sulfur dioxide fumes when exposed to air
Chemical Properties:
- pH: Extremely acidic; highly reactive with water and organic materials
- Solubility: Completely miscible with water (exothermic reaction)
- Oxidizing Properties: Acts as a strong oxidizing agent under certain conditions
- Corrosive Nature: Highly corrosive to metals and tissues
Description
Unlock the power of precision with Sulfuric Acid 98% ACS Grade, a top-tier laboratory reagent designed for a wide array of industrial, educational, and professional applications. With its high-purity formula, it is perfect for chemical synthesis, water treatment, and pH adjustments. Whether you’re working on an advanced laboratory experiment or managing industrial processes, our sulfuric acid ensures optimal results every time.
Applications for Sulfuric Acid 98% ACS Grade
Laboratory Applications
- Chemical Reagent: Used in titrations, pH adjustments, and other analytical procedures due to its high purity and consistency.
- Dehydrating Agent: Removes water from chemical reactions and organic compounds.
- Catalyst: Acts as a catalyst in esterification and other organic synthesis reactions.
Industrial Manufacturing
- Fertilizer Production: Essential in manufacturing phosphate fertilizers such as ammonium phosphate and superphosphate.
- Chemical Synthesis: Used to produce chemicals like hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, and sulfate salts.
- Petroleum Refining: Removes impurities during oil refining and cracking processes.
Water Treatment
- pH Adjustment: Neutralizes alkaline water to maintain the desired pH in industrial and municipal water treatment processes.
- Corrosion Control: Helps in preventing scale and rust in pipelines and equipment.
Batteries
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Serves as the electrolyte in automotive and industrial lead-acid batteries.
Cleaning and Descaling
- Industrial Cleaning: Removes rust, scale, and mineral deposits from metal surfaces and equipment.
- Pickling of Metals: Prepares metal surfaces for electroplating or painting by cleaning and removing oxidation.
Pharmaceuticals
- Synthesis of Drugs: Acts as a reagent in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical products.
Textile and Dye Industry
- Dyeing Process: Used in textile dyeing and bleaching operations.
- Synthetic Fiber Production: Plays a role in manufacturing synthetic fibers like rayon.
Food Industry
- Processing Aid: In regulated quantities, it can be used for food-grade applications, such as in the manufacture of gelatin.
Mining and Metallurgy
- Ore Processing: Extracts metals like copper, zinc, and uranium from their ores.
- Electrowinning: Used in electrolysis for metal recovery.
Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
- Etching Agent: Used in semiconductor manufacturing for etching and cleaning purposes.
Agriculture
- Soil Treatment: Adjusts soil pH in agricultural applications to improve crop yields.
Education
- Teaching Aid: Widely used in educational laboratories for chemistry experiments and demonstrations.
Storage:
- Temperature: Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area. Keep away from direct sunlight and heat sources to maintain stability.
- Container Material:
- Use corrosion-resistant containers such as glass, Teflon, or specific grades of plastic (e.g., HDPE).
- Avoid using metal containers or materials that react with acids.
- Sealing: Ensure containers are tightly closed to prevent moisture absorption, as sulfuric acid is highly hygroscopic.
- Segregation:
- Store separately from incompatible substances such as bases, organic materials, metals, reducing agents, and oxidizers.
- Maintain a dedicated storage area for acids to avoid accidental mixing with reactive chemicals.
- Secondary Containment: Use spill containment pallets or acid-resistant trays under storage containers to manage potential leaks or spills.
Handling:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Eye Protection: Wear chemical splash goggles or a full-face shield.
- Skin Protection: Use acid-resistant gloves (e.g., nitrile, neoprene), an acid-resistant apron, and protective clothing.
- Respiratory Protection: Use a respirator approved for acid fumes if working in poorly ventilated areas.
- Ventilation: Always handle sulfuric acid in a well-ventilated area or under a chemical fume hood to minimize exposure to fumes.
- Mixing:
- When diluting, always add acid to water slowly, never water to acid, to prevent a violent exothermic reaction and splattering.
- Use heat-resistant containers when diluting or mixing.
- Safe Practices:
- Avoid direct contact with skin, eyes, and clothing.
- Use non-sparking, acid-resistant tools and equipment.
- Do not eat, drink, or smoke while handling sulfuric acid.
Additional information
| SIZE | 100mL (3.3 Fl Oz), 250mL (8 Fl Oz), 500mL (16 Fl Oz), 1000mL (32 Fl Oz) |
|---|
Related products
-

Allyl Amyl Glycolate | Premium Fragrance/Aroma Compound
$16.00 – $29.99 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

1-Octanol (Alcohol C-8) Premium Aroma Fragrance Compound
$12.00 – $95.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
6-Methyl Coumarin | High-Purity Aroma & Industrial Compound
$12.99 – $19.99 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Methyl Alcohol (Methanol) – Premium Multi-Purpose Solvent
$12.99 – $70.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
SKU: N/A
Categories: Industrial Chemical, pH Regulator, Water Treatment
Tags: Applications of Sulfuric Acid 98% ACS Grade, Best Sulfuric Acid 98% Supplier Online, buy sulfuric acid, Buy Sulfuric Acid 98% Online, Certified ACS Grade Sulfuric Acid, Compliant Sulfuric Acid Packaging, Corrosion-Resistant Sulfuric Acid Packaging, GHS Labeled Sulfuric Acid, High-Concentration Sulfuric Acid 98%, High-Purity Sulfuric Acid, How to Safely Handle Sulfuric Acid, Industrial Sulfuric Acid 98%, Laboratory Grade Sulfuric Acid, Premium-Grade Sulfuric Acid, Reliable Sulfuric Acid for Industrial Use, Safe Handling Sulfuric Acid Solution, sulfuric acid 98%, Sulfuric Acid 98% ACS Grade, Sulfuric Acid 98% Near Me, Sulfuric Acid 98% Price, Sulfuric Acid 98% Supplier, sulfuric acid ACS certified, sulfuric acid ACS grade, sulfuric acid affordable pricing, sulfuric acid alternative applications, sulfuric acid analytical grade, sulfuric acid approved supplier, sulfuric acid bulk chemical, Sulfuric Acid Bulk Purchase, sulfuric acid bulk supplier, sulfuric acid catalyst, sulfuric acid chemical distribution, sulfuric acid chemical properties, sulfuric acid chemical reagent, sulfuric acid commercial use, sulfuric acid compatibility, sulfuric acid compliant chemical, sulfuric acid concentrated, sulfuric acid controlled substance, sulfuric acid cooling systems, sulfuric acid corrosion control, sulfuric acid custom formulations, sulfuric acid desiccant, sulfuric acid dilution process, sulfuric acid distributor, Sulfuric Acid Distributor in [Country/City], sulfuric acid domestic applications, sulfuric acid eco-friendly disposal, sulfuric acid excipient, sulfuric acid extreme pH chemical, sulfuric acid for academic research, sulfuric acid for acid rain simulation, sulfuric acid for agriculture, sulfuric acid for anodizing aluminum, sulfuric acid for battery electrolyte, Sulfuric Acid for Battery Maintenance, sulfuric acid for battery manufacturing, sulfuric acid for biodiesel production, sulfuric acid for cellulose processing, sulfuric acid for chemical engineering, sulfuric acid for chemical peeling, Sulfuric Acid for Chemical Synthesis, sulfuric acid for cleaning, Sulfuric Acid for Cleaning and Descaling, sulfuric acid for corrosion testing, sulfuric acid for dye manufacturing, sulfuric acid for electroplating, sulfuric acid for etching, sulfuric acid for ethanol production, Sulfuric Acid for Fertilizer Production, sulfuric acid for flue gas cleaning, sulfuric acid for fuel refining, sulfuric acid for gas scrubbing, sulfuric acid for glass manufacturing, sulfuric acid for gold recovery, sulfuric acid for hydrogen production, Sulfuric Acid for Industrial and Laboratory Use, sulfuric acid for industrial cleaning, sulfuric acid for inorganic chemistry, sulfuric acid for lab experiments, Sulfuric Acid for Laboratories, sulfuric acid for metal extraction, Sulfuric Acid for Mining Applications, Sulfuric Acid for Petroleum Refining, Sulfuric Acid for pH Adjustment, sulfuric acid for pH testing, sulfuric acid for pigment production, sulfuric acid for platinum refining, sulfuric acid for refining metals, sulfuric acid for resins, sulfuric acid for rust removal, Sulfuric Acid for Sale Near Me, sulfuric acid for science experiments, sulfuric acid for semiconductor processing, sulfuric acid for silver refining, sulfuric acid for soil pH correction, Sulfuric Acid for Textile Dyeing, sulfuric acid for wastewater treatment, Sulfuric Acid for Water Treatment, sulfuric acid fuming, sulfuric acid global supplier, sulfuric acid H2SO4, sulfuric acid hazardous chemical, sulfuric acid high purity, sulfuric acid high-concentration, sulfuric acid high-demand chemical, sulfuric acid highly reactive, sulfuric acid in agrochemicals, sulfuric acid in automotive industry, sulfuric acid in biochemistry, sulfuric acid in ceramics industry, sulfuric acid in chemical reactions, sulfuric acid in chlorine production, sulfuric acid in desulfurization, sulfuric acid in disinfectant manufacturing, sulfuric acid in electronics industry, sulfuric acid in explosives manufacturing, sulfuric acid in fertilizers, sulfuric acid in fuel cells, sulfuric acid in herbicides, sulfuric acid in hydrogenation, sulfuric acid in industrial labs, sulfuric acid in lead-acid batteries, sulfuric acid in leather processing, sulfuric acid in metal processing, sulfuric acid in mining, sulfuric acid in organic synthesis, sulfuric acid in paper industry, sulfuric acid in PCB manufacturing, sulfuric acid in pesticide formulations, sulfuric acid in petroleum refining, sulfuric acid in pharmaceuticals, sulfuric acid in phosphate processing, sulfuric acid in plastics manufacturing, sulfuric acid in power plants, sulfuric acid in rare earth processing, sulfuric acid in renewable energy, sulfuric acid in rocket propellants, sulfuric acid in rubber processing, sulfuric acid in steel pickling, sulfuric acid in sulfur fertilizers, sulfuric acid in textile processing, sulfuric acid in water treatment, sulfuric acid industrial applications, sulfuric acid industrial chemical, sulfuric acid industrial grade, sulfuric acid industrial solvent, sulfuric acid industrial uses, sulfuric acid international shipping, sulfuric acid lab safety, sulfuric acid lab-grade solutions, sulfuric acid laboratory chemical, sulfuric acid laboratory grade, sulfuric acid manufacturer, Sulfuric Acid Manufacturer [Region], sulfuric acid manufacturing processes, sulfuric acid material safety data sheet, sulfuric acid online purchase, sulfuric acid online supplier, sulfuric acid pH adjuster, sulfuric acid polymer industry, sulfuric acid price per kg, sulfuric acid product testing, sulfuric acid purity analysis, sulfuric acid quality assurance, sulfuric acid reagent for titration, sulfuric acid reagent grade, sulfuric acid regulations, sulfuric acid research and development, sulfuric acid research chemical, sulfuric acid restrictions, sulfuric acid safe handling practices, sulfuric acid safety handling, Sulfuric Acid Shipping Worldwide, sulfuric acid spill response, Sulfuric Acid Storage and Handling, sulfuric acid storage guidelines, sulfuric acid strong acid, sulfuric acid strong dehydrating agent, sulfuric acid strong oxidizer, sulfuric acid sulfur production, Sulfuric Acid Supplier in [Location], sulfuric acid supply chain, sulfuric acid technical applications, sulfuric acid technical grade, sulfuric acid transport regulations, sulfuric acid trusted supplier, sulfuric acid versatile applications, sulfuric acid wholesale, Sulfuric Acid with Safety Data Sheet (SDS), UN 1830 Sulfuric Acid Shipping, What is Sulfuric Acid 98% Used For?