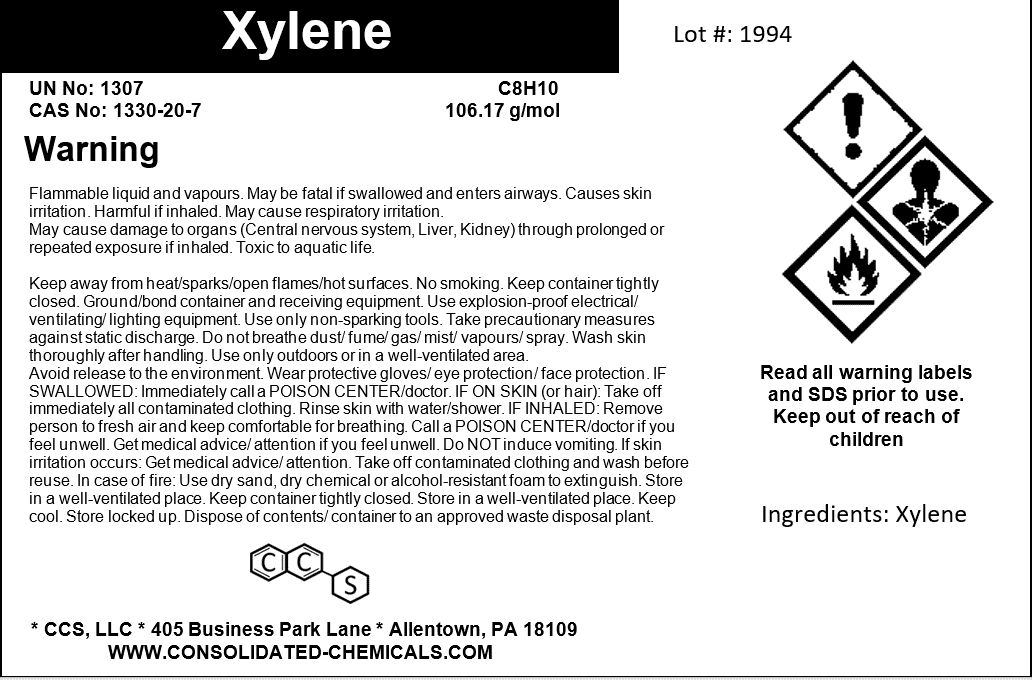
Xylene – Premium High-Purity Solvent
$14.99 – $29.99
General Information
- Chemical Name: Xylene (Mixed Isomers)
- Chemical Formula: C8H10
- CAS Number: 1330-20-7
- Molecular Weight: 106.17 g/mol
- Appearance: Clear, colorless liquid.
- Odor: Sweet, aromatic hydrocarbon odor.
Physical Properties
- Density: 0.86–0.87 g/cm³ at 20°C.
- Boiling Point: 137–140°C (varies by isomer).
- Melting Point: -47.4°C (varies by isomer).
- Flash Point: ~27°C (closed cup).
- Refractive Index: 1.497–1.501 at 20°C.
- Vapor Pressure: 8–9 mmHg at 20°C.
- Solubility:
- Insoluble in water (~0.015% at 25°C).
- Soluble in ethanol, ether, acetone, and most organic solvents.
Chemical Properties
- Purity: Typically ≥ 99% for industrial and laboratory-grade xylene.
- Isomer Content: Mixture of ortho-xylene, meta-xylene, and para-xylene.
- Stability:
- Stable under normal conditions.
- Avoid strong oxidizing agents and open flames.
- Flammability: Highly flammable liquid and vapor.
Description
Xylene is a colorless, flammable liquid hydrocarbon characterized by a sweet aromatic odor. It consists of three isomers: ortho-xylene, meta-xylene, and para-xylene, collectively referred to as mixed xylene. Known for its excellent solvency properties, xylene is widely used in various industrial and commercial applications.
In the paint and coatings industry, xylene serves as a solvent, enhancing the application and drying properties of products. It is also utilized in the production of adhesives, printing inks, and in the formulation of cleaning agents. As a chemical intermediate, xylene is essential in manufacturing key compounds like terephthalic acid, which is used to produce polyester fibers and resins.
Applications:
Paints, Coatings, and Solvents
- Paint Thinner:
- Commonly used as a thinner for oil-based paints and varnishes, improving flow and consistency.
- Coating Solvent:
- A key solvent in coatings, including industrial and automotive paints, due to its excellent solvency properties.
- Adhesives and Sealants:
- Used in the formulation of adhesives and sealants for improved application and drying.
Printing and Ink Industry
- Printing Inks:
- Acts as a solvent in the production of printing inks to enhance flow and drying performance.
- Marker Pen Ink:
- Found in permanent marker formulations for its quick-drying properties.
Cleaning and Degreasing
- Industrial Cleaning Agent:
- Effective for cleaning machinery, tools, and surfaces, particularly in removing grease and oil.
- Electronics Industry:
- Used to clean circuit boards and electronic components during manufacturing.
Chemical Industry
- Intermediate in Chemical Synthesis:
- Serves as a precursor or solvent in the production of chemicals like terephthalic acid, phthalic anhydride, and isophthalic acid.
- Polymer Production:
- Used in the synthesis of polymers and resins, including polyesters and epoxies.
Petroleum Industry
- Octane Booster:
- Added to gasoline to improve octane rating and engine performance.
- Oil Extraction:
- Used in petrochemical extraction processes to separate oil from other components.
Laboratory and Research
- Analytical Solvent:
- Utilized in laboratories for analytical procedures such as chromatography.
- Histology and Pathology:
- Used in tissue preparation and staining processes to clear samples and remove paraffin wax.
Rubber and Plastics Industry
- Rubber Processing:
- Acts as a solvent in rubber formulations, aiding in processing and application.
- Plastic Production:
- Used in the production of polystyrene and other plastics.
Construction and Engineering
- Concrete Sealers and Curing Compounds:
- Added to concrete sealers to improve penetration and bonding properties.
- Metal Cleaning:
- Employed to remove rust, grease, and other contaminants from metal surfaces.
Printing and Packaging
- Packaging Materials:
- A solvent in the production of flexible packaging materials and laminates.
- Printing Films:
- Used in the formulation of films and coatings for packaging.
Miscellaneous Applications
- Aerospace Industry:
- Used as a cleaning solvent for aerospace components due to its powerful degreasing properties.
- Textile Industry:
- Used in dyeing and finishing textiles for improved penetration and dye fastness.
Storage Conditions:
- Store in a cool, well-ventilated area, away from heat sources, open flames, and oxidizing agents.
Safety and Handling:
- Hazards: Flammable, harmful if inhaled or absorbed through the skin. Appropriate PPE should be used.
- Stability: Stable under normal conditions, but can react with strong oxidizing agents.
Additional information
| Size | 250mL (8 Fl Oz), 500mL (16 Fl Oz), 1000mL (32 Fl Oz) |
|---|
Related products
-

Glycol Ether PM (Propylene Glycol Mono Methyl Ether)
$10.00 – $265.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Amyl Acetate 99% – Food Grade – Industrial and Laboratory Solvent
$9.99 – $290.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Pyridine – High-Purity Solvent
$18.00 – $24.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Anethole | High-Purity Flavor & Fragrance Compound
$12.99 – $65.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page